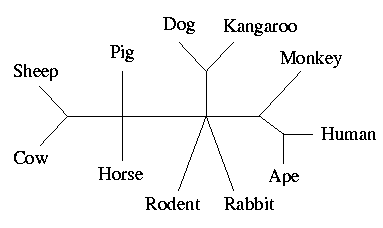

Most of the inferred inter-species relationships coincide with what is expected, e.g., primates (human, gorilla, ape) and ungulates (cow, sheep, pig, horse). The Dog-Kangaroo group, also inferred by other methods, such as Neighbor Joining (Penny et al 91) and Maximum Parsimony, may be suspected of being incorrect, but Penny et al (91) report that they did not reach any firm conclusion concerning that edge.
The Qstar program takes here no decision concerning the
position of the rodent and the rabbit, in relation to the other
mammals. To date, there is no strong consensus on the position of the
rodent and the recent polemic concerns the possibility of the rodent
being at the root of the mammalian evolution (Graur et al 91,
Erchia et al 96).