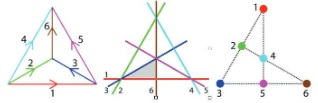
 Three dimentional reconstruction of subcutaneous tissue
Three dimentional reconstruction of subcutaneous tissue 3D geometrical and biomechanical modelling of the skin/subcutaneous complex
The aim of this project is to build a 3D geometric and mechanical model of the skin/subcutaneous complex (SSC) which could be adapted to the different parts of the body and to the morphological parameters of the patient.
Three-dimensional study of the skin/subcutaneous complex using in vivo whole body
Generic 3D Geometrical and Mechanical Modeling of the Skin/Subcutaneous Complex by a Procedural Hybrid Method
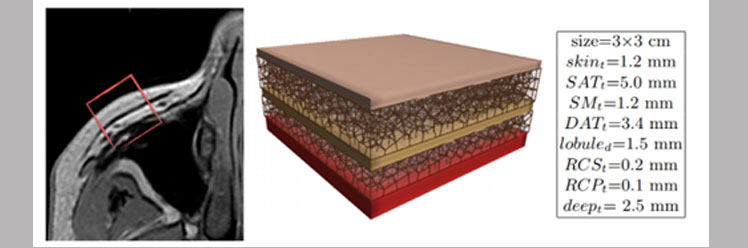
 Identificaiton of points of difference between shapes of human skull and monkey skull
Identificaiton of points of difference between shapes of human skull and monkey skullCombinatorial structures and applications
A recent pioneering applied work, in collaboration between the ICAR team and the ALGCO team, has shown that oriented matroids can be used efficiently to encode, analyze, characterize and classify shapes of 3D models given by point configurations.
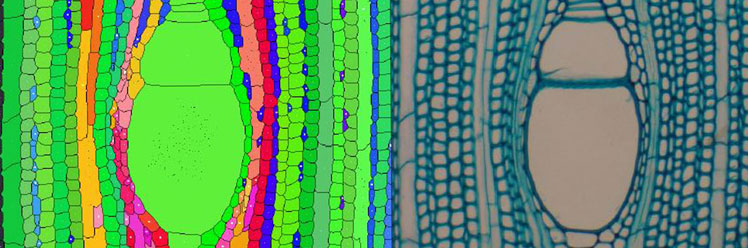 Détection automatique des files cellulaires dans des images microscopiques de coupes de bois (collaboration avec AMAP/CIRAD)
Détection automatique des files cellulaires dans des images microscopiques de coupes de bois (collaboration avec AMAP/CIRAD)
Visualization and identification : application to natural objects; Wood cell identification, tree segmentation
The analysis of anatomical sections of wood provides important information for understanding the secondary growth and development of plants. This study reports on a new method for the automatic detection and characterization of cell les in wood images obtained by light microscopy.
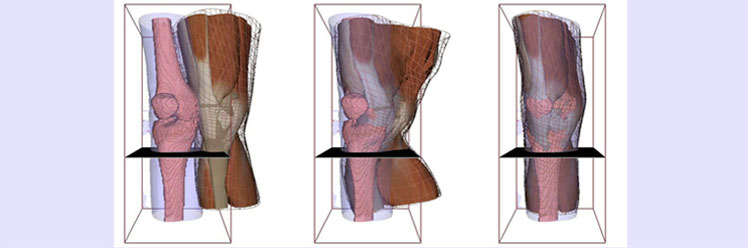 Modélisation personnalisée d'un genou par recalage d'un modèle déformable sur des données 'scanner'
Modélisation personnalisée d'un genou par recalage d'un modèle déformable sur des données 'scanner'
Anatomical modeling (skin and muscle)
We developed a novel approach for simulating 3D muscle deformations with complex architectures. The approach consists in choosing the best model formulation in terms of computation cost and accuracy, that mixes a volumetric tissue model based on finite element method (3D FEM), a muscle fiber model (Hill contractile 1D element) and a membrane model accounting for aponeurosis tissue (2D FEM).